Q1. What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder. It is a partial or complete stopping of breath during sleep. This causes the body to strain harder for oxygen, and makes the brain send signals that jerk your body awake to resume proper breathing. There are 3 types of sleep apneas: Obstructive, Central and Complex.
Q2. What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)?
Obstructive Sleep Apnea is the most common type of sleep apnea. This form of disorder occurs due to partial or even complete airway blockage during sleep. The airway becomes covered usually by the tongue due to abnormal muscle relaxation of the tongue and surrounding muscles in the throat area. This results in shallow breath and even stoppage of breathing while asleep. The oxygen level in the body drops and heart rate increases. This lowered oxygen level is dangerous and can cause stroke or heart attack. The most common characteristic of OSA is snoring.
Q3. What is Central Sleep Apnea?
In Central Sleep Apnea, the breathing repeatedly stops and starts due to improper signaling from the brain. Although the muscles that control breathing do not over relax or obstruct the air path, they do not get appropriate signals from the brain and as a result breathing is disrupted.
Q4. What is Complex Sleep Apnea?
Complex Sleep Apnea is a combination of Obstructive and Central Sleep Apnea.
Q5. What are the warning signs of Sleep Apnea?
The most common sign of OSA is loud snoring, loud enough to disturb the sleep of patient as well as others. It is important to note that not everyone who snores suffers from OSA
• Depression
Q6. What causes snoring?
Snoring is most often caused by loose, weak, or excessive tissue at the back of the throat which collapses into the airway during sleep. This tissue flutters or vibrates as air is breathed in. This fluttering tissue, like a flag flapping in a strong breeze is the cause of the aggravating noise we know as snoring.
Q7. What can happen if sleep apnea goes untreated?
If untreated sleep apnea can disrupt your daily life, overall health and productivity and lead to the following:
Q8. Who is at risk for Sleep Apnea?
Q9. How is Sleep Apnea diagnosed?
If you have symptoms of sleep apnea or other sleep disorder, your doctor may require you to have a sleep study test called a Polysomnogram. The test will help to determine the type and severity of sleep apnea or sleep disorder. A sleep study is an overnight test where you sleep in a sleep lab or medical facility that is specifically equipped to be as comfortable as possible while still monitoring your sleep. The sleep study test involves sensors that monitors your heart rate, breathing, blood oxygen level, brain waves and more.
A home sleep apnea test is similar to an overnight sleep study test, but it doesn’t involve brain wave monitoring. This test cannot diagnose central sleep apnea, and it is usually not an option when providers suspect more serious sleep disorder.
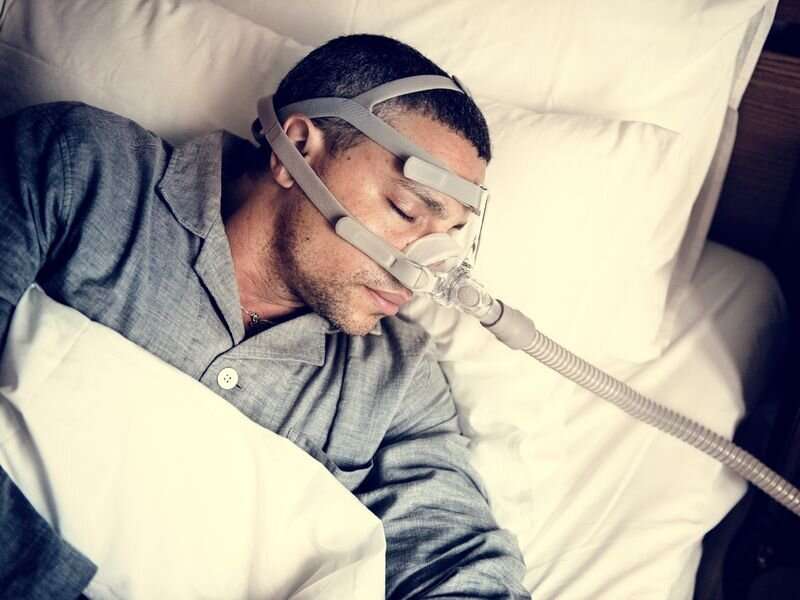
Q10. What is the treatment for Sleep Apnea?
Treatments for sleep apnea depend on the specific type of sleep apnea and how severe it is. Some treatment may include behavioral measures such as weight loss, exercise, stop smoking, and sleeping on one’s side or back. Positive Airway Pressure (PAP) is a method that uses a specialized device to increase the air pressure inside of your airway while you inhale. The best- known PAP device is the Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machine. CPAP is the most common treatment as it provides constant air pressure in your throat to keep the airway open when you breathe in.
Source: Dr. Kevin Moss

You can take the Sleep Apnea Screening Questionnaire here.